Rf Attenuation Building Materials
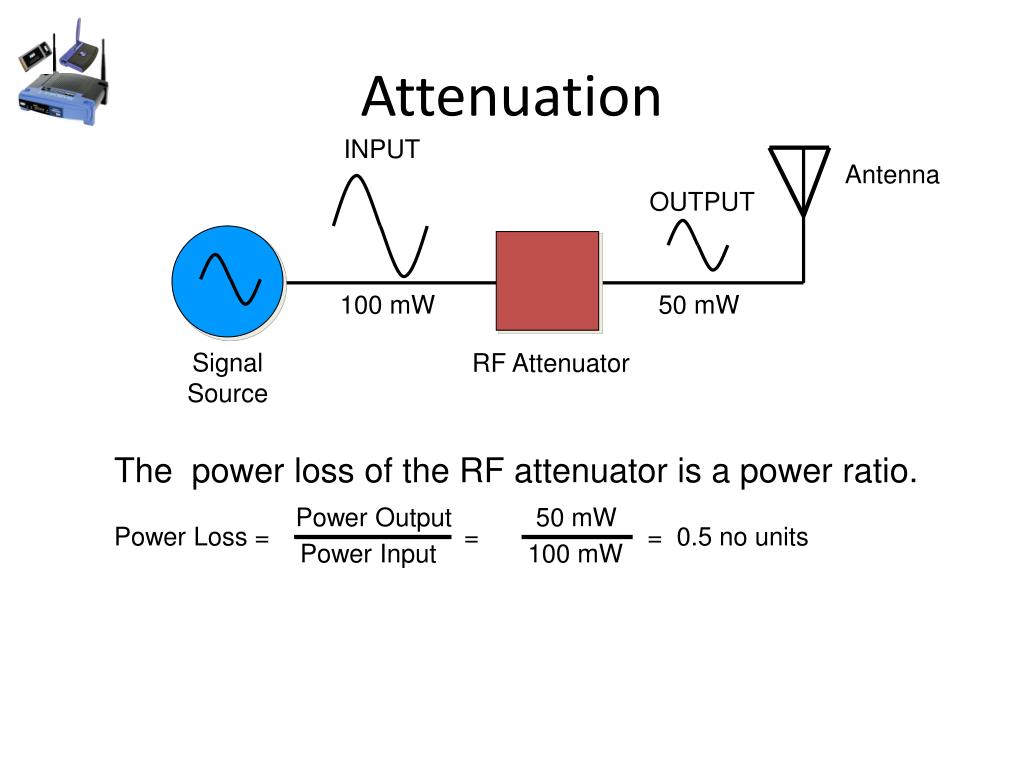
The complex permittivity can be written as 1 1 tan 0 r r j e r j we s e e where σ is the conductivity of the material and tan is known as.
Rf attenuation building materials. Elevator or metal obstacle 10 db. In this section theoretical effects of material electrical properties and structure on radio wave propagation will be discussed. The materials investigated included brick masonry block eight different concrete mixes glass plywood lumber spruce pine fir drywall reinforced concrete steel reinforcing bar grids variations of the plywood and lumber tests in which the specimens were soaked with water and composite specimens involving brick faced masonry block and brick faced concrete. In the ibwave database of components there are several different types of glass listed for used during modeling.
Metal rack 6 db. Nontinted glass windows 3 db. Cubicle wall 2 db. Foundation wall 15 db.
Brick concrete concrete blocks 12 db. R therefore the phase and attenuation of an electromagnetic wave passing through a homogenous dielectric material in free space are fully determined by their complex permittivity. Staying focused on materials commonly used when modeling a venue a couple of material families started to stand out to me when looking at the range of attenuation values across the different types. 2 1 theory of material electrical properties.
Wood door 3 db. Radio waves that interact with a building will produce losses that depend on the electrical properties of the building materials and material structure. According to the cwna official study guide attenuation of building materials is as follows for 2 4 ghz.